In the realm of industrial computing, the demand for reliable and robust systems that can operate in harsh environments is ever-increasing. Whether it's in the form of automated picking arms in automotive plants, self-driven mining machines, or automated drilling, intelligent manufacturing and railway operations, these compact robust industrial pc systems offer the dependability and performance that industries require.
This demand has led to the development of fanless embedded industrial computers, which offer a unique set of advantages over their actively cooled counterparts. One of the key challenges in designing these systems is effective heat management without the use of fans. In this article, we will explore the sources of heat and cooling systems in industrial computers.
Sources of Heat in Industrial Computers
The primary sources of heat in a computer system include the CPU, GPU, Chippset, Voltage Regulator Modules, Memory Module, NIC, LAN Controller, and other components that generate heat due to their operation.
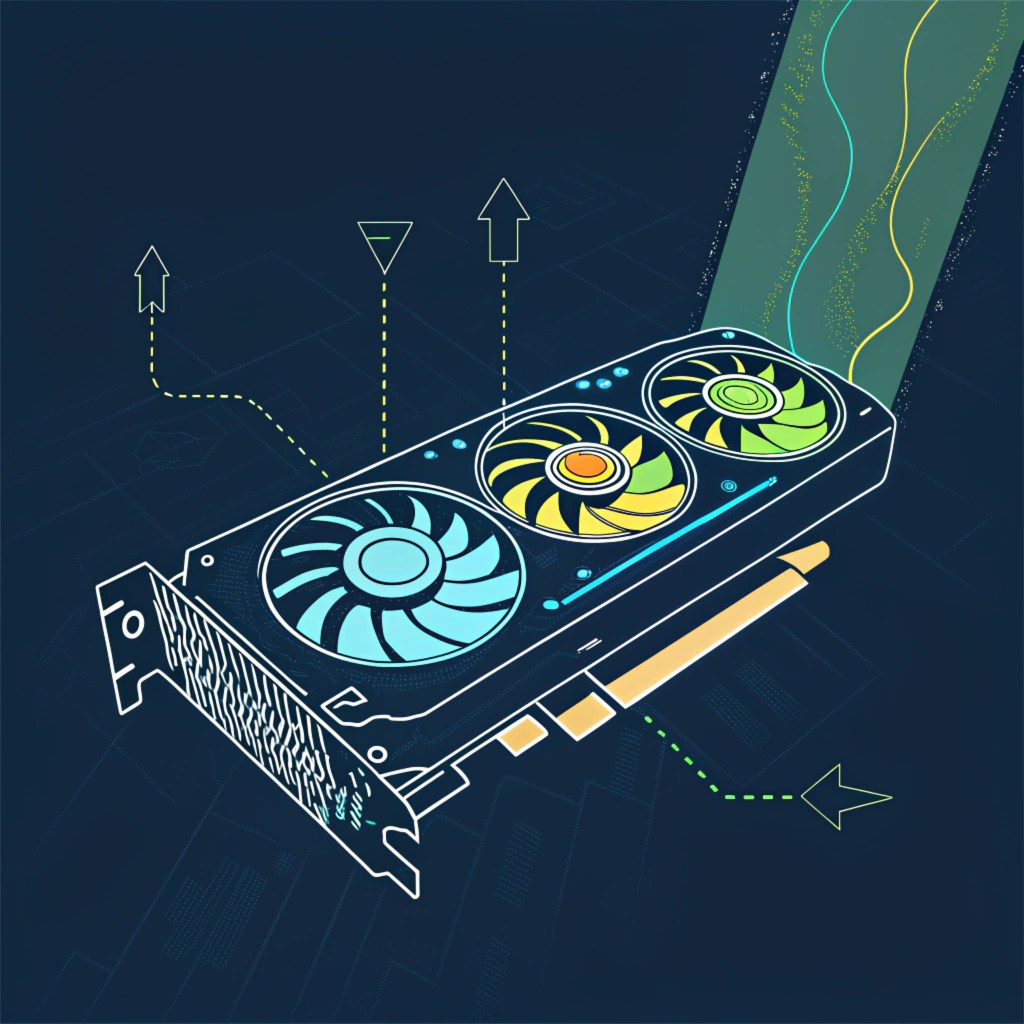
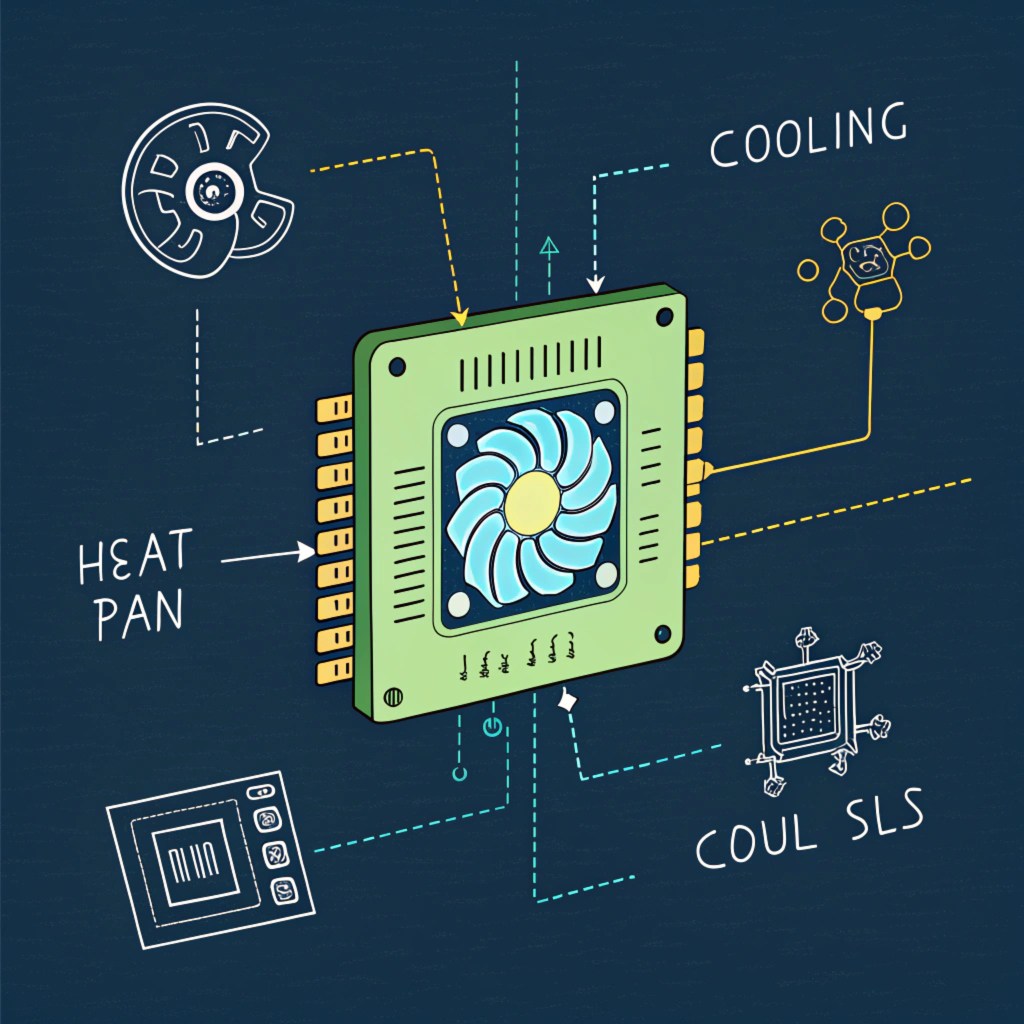


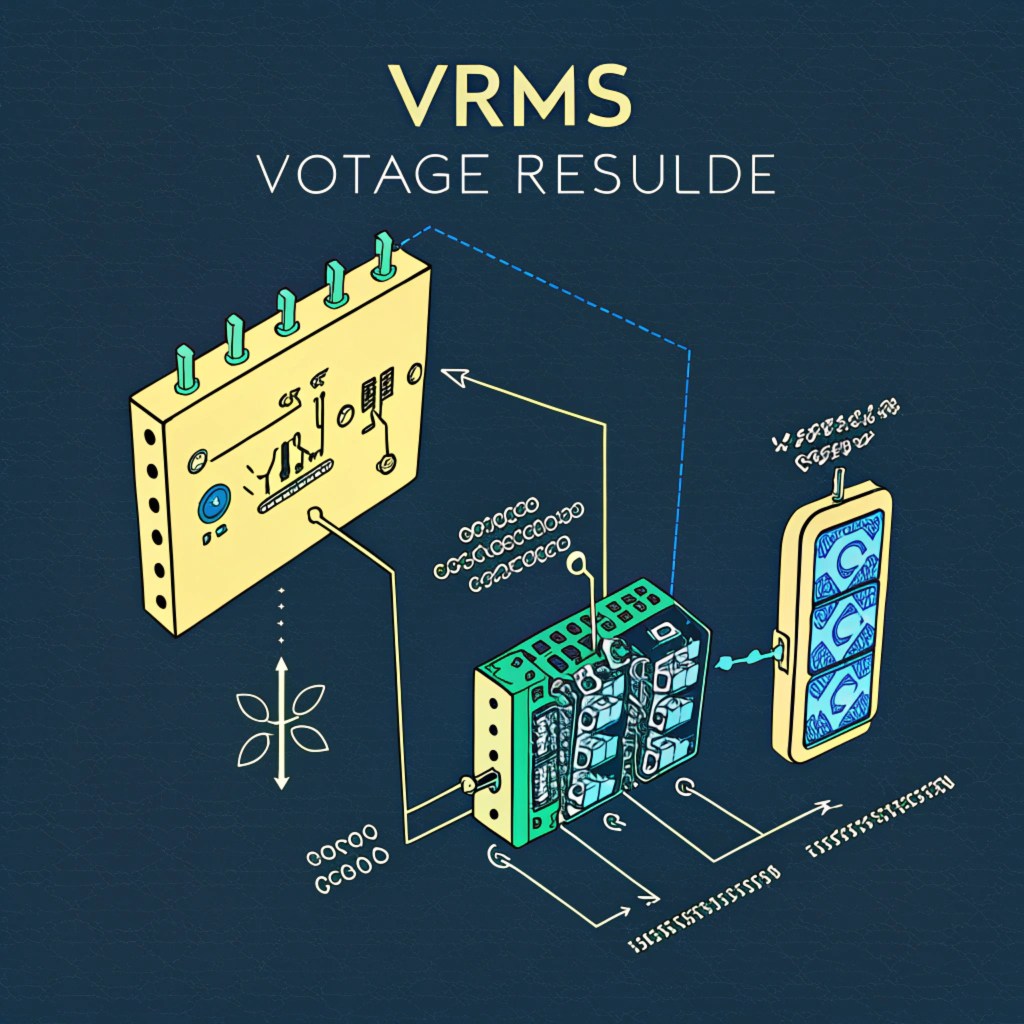
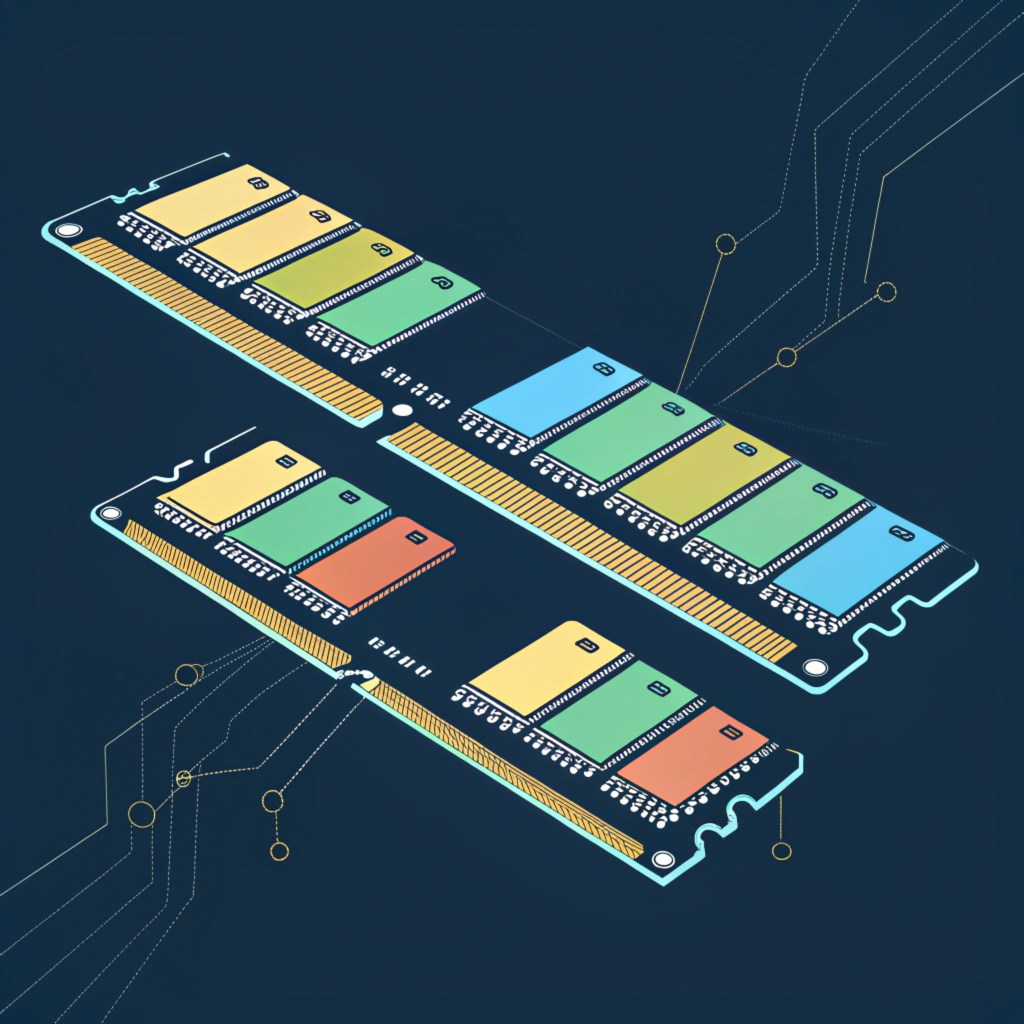
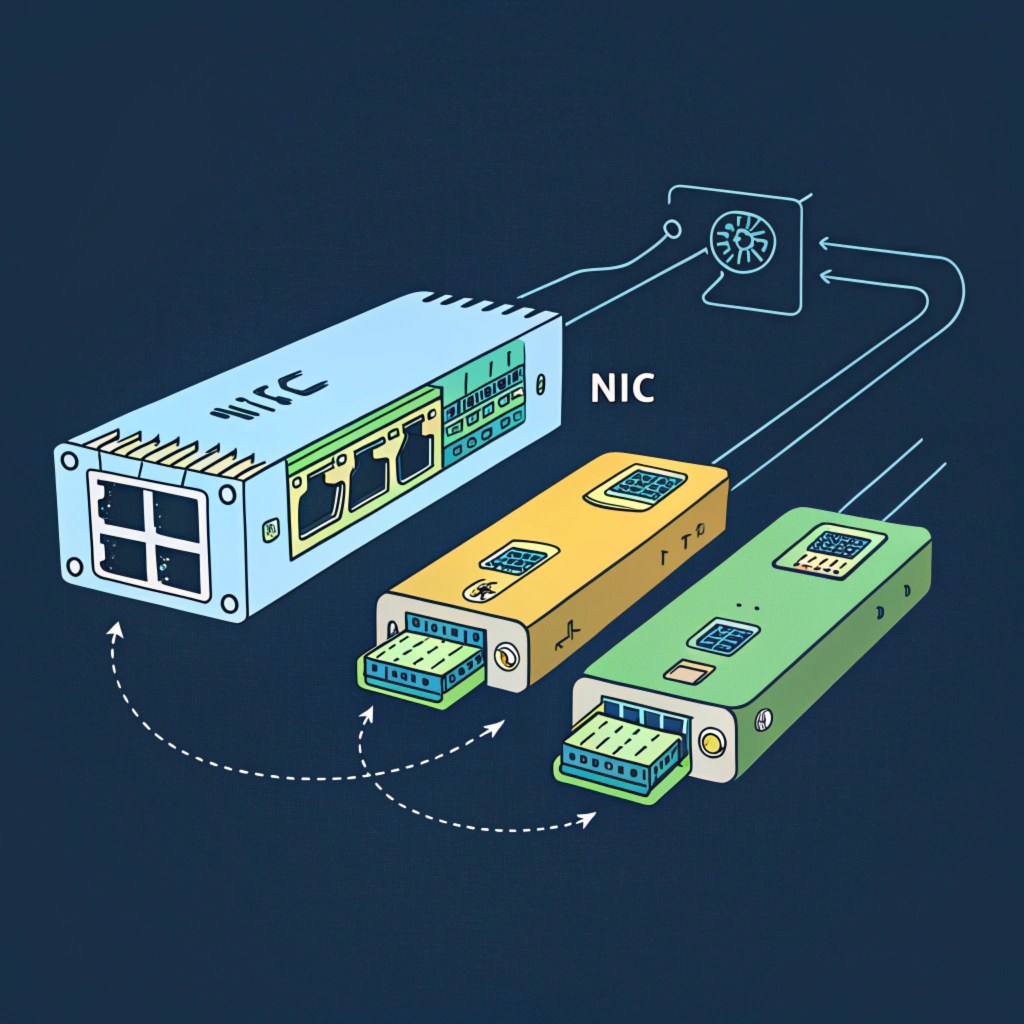
The Importance of Passive Cooling Design
High temperatures can significantly impact the lifespan of computer components and may lead to thermal shutdowns or CPU throttling, resulting in reduced performance. Striking a balance between performance and heat dissipation is crucial, and different embedded computer manufacturers have their unique approaches to this challenge. The cooling methods of industrial computers are mainly divided into active cooling and passive cooling. Active cooling usually includes cooling fans to reduce the heat energy of computer parts, while passive cooling uses special heat dissipation structure design to quickly remove heat energy from the host.
The Pros and Cons of Active Cooling System
 High Heat Dissipation
High Heat Dissipation
 Performance
Performance
 Dust and Debris
Dust and Debris
The Pros and Cons of Passive Cooling System Computers
Advantages:
1. Silence: Since there are no moving parts, passive cooling systems are completely make them as silence industrial mini computers.
2. Reliability: With no moving parts to fail, Windows 11 Compatible Fanless PCs with passive cooling systems are more reliable and have a longer lifespan.
3. Dust and Debris Resistance: The absence of fans means there's less chance of dust and debris entering the system, reducing the risk of component damage.
4. Energy Efficiency: Passive cooling systems do not consume additional power, making them more energy-efficient.
5. Suitable for Harsh Environments: Wide temperature Industrial PCs can operate effectively in environments where dust, moisture, or other factors might damage active cooling components.
Disadvantages:
1. Limited Heat Dissipation: Passive cooling may not be as effective for components that generate a lot of heat.
2. Size and Design Constraints: Effective passive cooling often requires careful design and may result in larger or more complex systems.
In environments where silence is required, such as in medical facilities, laboratories, or control rooms, passive cooling is the preferred choice. Its reliability and low maintenance requirements make it ideal for long-term, unattended operations, which are common in industrial settings. The resistance to dust and debris infiltration is particularly beneficial in harsh or dirty environments, such as factories or construction sites, where fan-based cooling systems would be at risk of rapid degradation.
Proper heat management industrial computer is essential to prevent damage to electronic components, extend the life of the system, and maintain performance. Conversely, inadequate heat management can lead to system instability, reduced reliability, and even safety incidents. In the next article, we will continue to analyze the passive cooling fanless PC solution provided by Fodenn IPC R&D Manufacturer. Discuss with Fodenn's technicians and Stay tuned~